Over the past century, Marxism has been radically transformed
in line with circumstances and fashion. Theses that once looked solid have
depreciated and fallen by the sideline; concepts that once were deemed
crucial have been abandoned; slogans that once sounded clear and
meaningful have become fuzzy and ineffectual.
But two key words seem to have survived the attrition and
withstood the test of time: imperialism and
financialism.[1]
Talk of imperialism and financialism – and particularly of the
nexus between them – remains as catchy as ever. Marxists of different
colours – from classical, to neo to post – find the two terms expedient,
if not indispensable. Radical anarchists, conservative Stalinists and
distinguished academics of various denominations all continue to use and
debate them.
The views of course differ greatly, but there is a common
thread: for most Marxists, imperialism and financialism are prime causes
of our worldly ills. Their nexus is said to explain capitalist development
and underdevelopment; it underlies capitalist power and contradictions;
and it drives capitalist globalization, its regional realignment and local
dynamics. It is a fit-all logo for street demonstrators and a generic
battle cry for armchair analysts.
The secret behind this staying power is flexibility. Over the
years, the concepts of imperialism and financialism have changed more or
less beyond recognition, as a result of which the link between them
nowadays connotes something totally different from what it meant a century
ago.
The purpose of this article is to outline this chameleon-like
transformation, to assess what is left of the nexus and to ask whether
this nexus is still worth keeping.
Empire and Finance
The twin notions of imperialism and financialism emerged at the
turn of the twentieth century. The backdrop is familiar enough. During the
latter part of the nineteenth century, the leading European powers were
busy taking over large tracts of non-capitalist territory around the
world. At the same time, their own political economies were being
fundamentally transformed. Since the two developments unfolded hand in
hand, it was only natural for theorists to ask whether they were related –
and if so, how and why.
The most influential explanation came from a British left
liberal, John Hobson, whose work on the subject was later extended and
modified by Marxists such as Rosa Luxemburg, Rudolf Hilferding, Vladimir
Lenin and Karl Kautsky, among others.[2]
Framed in a nutshell, the basic argument rested on the belief
that capitalism had changed: originally ‘industrial’ and ‘competitive’,
the system had become ‘financial’ and
‘monopolistic’.
This transformation, said the theorists, had two crucial
effects. First, the process of monopolization and the centralization of
capital in the hands of the large financiers made the distribution of
income far more unequal, and that greater inequality restricted the
purchasing power of workers relative to the productive potential of the
system. As a result of this imbalance, there emerged the spectre of
‘surplus capital’, excess funds that could not be invested profitably in
the home market. And since this ‘surplus capital’ could not be disposed of
domestically, it forced capitalists to look for foreign outlets,
particularly in pristine, pre-capitalist regions.
Second, the centralization of capital altered the political
landscape. Instead of the night-watchman government of the laissez-faire
epoch, there emerged a strong, active state. The laissez-faire capitalists
of the earlier era saw little reason to share their profits with the state
and therefore glorified the frugality of a small central administration
and minimal taxation. But the new state was no longer run by hands-off
liberals. Instead, it was dominated and manipulated by an aggressive
oligarchy of ‘finance capital’ – a coalition of large bankers, leading
industrialists, war mongers and speculators who needed a strong state that
would crack down on domestic opposition and embark on foreign military
adventures.
And so emerged the nexus between imperialism and financialism.
The concentrated financialized economy, went the argument, requires
pre-capitalist colonies where surplus capital can be invested profitably;
and the cabal of finance capital, now in the political driver’s seat, is
able to push the state into an international imperialist struggle to
obtain those colonies.
At the time, this thesis was not only totally new and highly
sophisticated; it also fit closely with the unfolding of events. It gave
an elegant explanation for the imperial bellicosity of the late nineteenth
century, and it neatly accounted for the circumstances leading to the
great imperial conflict of the first ‘World War’. There were of course
other explanations for that war – from realist/statist, to liberal, to
geopolitical, to psychological.[3] But for most intellectuals, these
alternative explications seemed too partial or instrumental compared to
the sweeping inevitability offered by the nexus of empire and
finance.
History, though, kept changing, and soon enough both the theory
and its basic concepts had to be altered.
Monopoly Capital
The end of the Second World War brought three major
transformations. First, the nature of international conflict changed
completely. Instead of a violent inter-capitalist struggle, there emerged
a Cold War between the former imperial powers on the one hand and the
(very imperial) Soviet bloc on the other (with plenty of hot proxy
conflicts flaring up in the outlying areas). Second, the relationship
between core and periphery was radically altered. Outright conquest and
territorial imperialism gave way to decolonization, while tax-collecting
navies were replaced by the more sophisticated tools of foreign aid and
foreign direct investment (FDI). Third and finally, the political
economies of the core countries themselves were reorganized. Instead of
the volatile laissez-faire regime, there arose a large welfare-warfare
state whose ‘interventionist’ ideologies and counter-cyclical policies
managed to reduce instability and boost domestic
growth.
On the face of it, this new constellation made talk of
finance-driven imperialism seem outdated if not totally irrelevant. But
the theorists didn’t give up the nexus. Instead, they gave it a new
meaning.
The revised link was articulated most fully by the Monopoly
Capital School associated with the New York journal Monthly Review.[4]
Capitalism, argued the writers of this school, remains haunted by a lack
of profitable investment outlets. And that problem, along with its
solution, can no longer be explained in classical Marxist
terms.
The shift from competition to oligopoly that began in the late
nineteenth century, these writers claimed, was now complete. And that
shift meant that Marx’s ‘labour theory of value’ and his notion of
‘surplus value’ had become more or less irrelevant to capitalist
pricing.
In the brave new world of oligopolies, the emphasis on
non-price competition speeds up the pace of technical change and
efficiency gains, making commodities cheaper and cheaper to produce. But
unlike in a competitive system, these rapid cost reductions do not
translate into falling prices. The prevalence of oligopolies creates a
built-in inflationary bias which, despite falling costs, makes prices move
up and sometimes sideways, but rarely if ever down.
This growing divergence between falling costs and rising prices
increases the income share of capitalists, and that increase reverses the
underlying course of capitalism. Marx believed that the combination of
ever-growing mechanization and ruthless competition creates a ‘tendency of
the rate of profit to fall’. But the substitution of monopoly capitalism
for free competition inverts the trajectory. The new system is ruled by an
opposite ‘tendency of the surplus to rise’.
The early theorists of imperialism, although using a different
vocabulary, understood the gist of this transformation. And even though
they did not provide a full theory to explain it, they realized that the
consequence of that transformation was to shift the problem of capitalism
from production to circulation (or in later Keynesian parlance, from
‘aggregate supply’ to ‘aggregate demand’). The new capitalism, they
pointed out, suffered not from insufficient surplus, but from too much
surplus, and its key challenge now was how to ‘offset’ and ‘absorb’ this
ever-growing excess so that accumulation could keep going instead of
coming to a halt.
That much was already understood at the turn of the twentieth
century. But this is where the similarity between the early theorists of
imperialism and the new analysts of Monopoly Capital
ends.
Black Hole: The Role of Institutionalized
Waste
Until the early twentieth century, it seemed that the only way
to offset the growing excess was productive and external: the surplus of
goods and capital had to be exported to and invested in pre-capitalist
colonies. But as it turned out, there was another solution, one that the
early theorists hadn’t foreseen and that the analysts of Monopoly Capital
now emphasized. The surplus could also be disposed off unproductively and
internally: it could be wasted at home.
For the theorists of Monopoly Capital, ‘waste’ denoted
expenditures that are necessary neither for producing the surplus nor for
reproducing the population, and that are, in that sense, totally
unproductive and therefore wasteful. These expenditures absorb existing
surplus without ever creating any new surplus, and this double feature
enables them to mitigate without ever aggravating the ‘tendency of the
surplus to rise’.
The absorptive role of wasteful spending wasn’t entirely new,
having already been identified at the turn of the twentieth century by
Thorstein Veblen.[5] But it was only after the Second Word War, with the
entrenchment of the Fordist model of mass production and consumption and
the parallel rise of the welfare-warfare state, that the process was fully
and conscientiously institutionalized as a salient feature of monopoly
capitalism.
By the end of the war, the U.S. ruling class grew fearful that
demobilization would trigger another severe depression; and having
accepted and internalized the stimulating role of large-scale government
spending, it supported the creation of a new ‘Keynesian Coalition’ that
brought together the interests of big business, the large labour unions
and various state agencies. The hallmark of this coalition was
immortalized in a secret U.S. National Security Council document (NSC-62),
whose writers explicitly called on the government to use high military
spending as a way of securing the internal stability U.S.
capitalism.[6]
According to its theorists, monopoly capitalism gave rise to
many forms of institutionalized waste – including a bloated sales effort,
the creation of new ‘desires’ for useless goods and services and the
acceleration of product obsolescence, among other strategies. But the two
most significant types of waste were spending on the military and on the
financial sector.
The importance of these latter expenditures, went the argument,
lies in their seemingly limitless size. The magnitude of military
expenditures has no obvious ceiling: it depends solely on the ability of
the ruling class to justify the expenditures on grounds of national
security. Similarly with the size of the financial sector: its magnitude
expands with the potentially limitless inflation of credit. This
convenient expandability turns military spending and financial
intermediation into a giant ‘black hole’ (our term): they suck in large
chunks of the excess surplus without ever generating any excess surplus of
their own.[7]
Now, on the face of it, the efficacy of this domestic black
hole should have made imperialism less necessary if not wholly redundant.
According to the theorists of Monopoly Capital, though, this would be the
wrong conclusion to draw. It is certainly true that, unlike the old
imperial system, monopoly capitalism no longer needs colonies. But the
absence of formal colonies is largely a matter of appearance. Remove this
appearance and you’ll see the imperial impulse pretty much intact: the
core continues to exploit, dominate and violate the periphery for its own
capitalist ends.[8]
Spearheaded by U.S.-based multinationals and no longer hindered
by inter-capitalist wars, argued the theorists, the new order of monopoly
capitalism has become increasingly global and ever more integrated. And
this global integration, they continued, has come to depend on an
international division of labour, free access to strategic raw materials
and political regimes that are ideologically open for business. However,
these conditions do not develop automatically and peacefully. They have to
be actively promoted and enforced – often against stiff domestic
opposition – and they have to be safeguarded against external threats (the
Soviet bloc before its collapse, Islamic fundamentalism and rogue states
since then, etc.). And because such promotion and enforcement hinge on the
threat and frequent use of violence, there is an obvious justification if
not outright need for a large, well-equipped army sustained by large
military budgets.
In this context, military spending comes to serve a dual role:
together with the financial sector and other forms of waste, it propels
the accumulation of capital by black-holing a large chunk of the economic
surplus; and it helps secure a more sophisticated and effective
neo-imperial order that no longer needs colonial territories but is every
bit as expansionary, exploitative and violent as its crude imperial
predecessor.
Dependency
This dependency, went the argument, is the outcome of five
hundred years of colonial destruction. During that period, the imperial
powers systematically undermined the socio-economic fabric of the
periphery, making it totally dependent on the core. In this way, when
decolonization finally started, the periphery found itself unable to take
off while the capitalist core prospered. There was no longer any need for
core states to openly colonize and export capital to the periphery. Using
their disproportionate economic and state power, the former imperialist
countries were now able to hold the postcolonial periphery in a state of
debilitating economic monoculture, political submissiveness and cultural
backwardness – and, wherever they could, to impose on it a system of
unequal exchange.
Unequal exchange can take different forms. It may involve a
wage gap between the ‘less exploited’ labour aristocracy of the core and
the ‘more exploited’ simple labour of the periphery. Or the core can
compel the periphery to buy its exports at ‘high’ prices (relative to
their ‘true’ value), while importing the periphery’s products at ‘low’
prices (relative to their ‘true’ value). As a result of this latter
difference, the terms of trade get ‘distorted’, surplus is constantly
siphoned into the core (rather than exported from or domestically absorbed
by the core), and the eviscerated periphery remains chronically
underdeveloped.[10]
This logic of dependent underdevelopment was first articulated
during the 1950s and 1960s as an antidote to the liberal modernization
thesis and its Rostowian promise of an imminent takeoff.[11] And at the
time, that antidote certainly seemed to be in line with the chronic
stagnation of peripheral countries.
But what started as a partial theory soon expanded into a
sweeping history of world capitalism. According to this broader narrative,
capitalism was and remained imperial from the word go: it didn’t simply
start with conquest; it started because of conquest. Its very inception
was predicated on geographical exploitation and domination – a process in
which the financial-commercial metropolis (say England) used the surplus
extracted from a productive periphery (say India) to kick-start its own
economic growth. And once started, the only way for this growth to be
sustained is for the metropolis to continue to eviscerate the periphery
around it. The development of the emperor depends on and necessitates the
underdevelopment of its subjects.
The next theoretical step was to fit this template into an even
broader concept of a World System – an all-encompassing global approach
that seeks to map the hierarchical political relationships, division of
labour and flow of commodities and surplus between the peripheral
countries at the bottom, the semi-peripheral satellites in the middle and
the financial core at the apex. From the viewpoint of this larger
retrofit, capitalism is no longer the outcome of a specific class
struggle, a conflict that developed in Western Europe during the twilight
of feudalism and later spread to and reproduced itself in the rest of the
world. Instead, capitalism – to the extent that this term can still be
meaningfully used – is merely the outer appearance of Europe’s imperial
expedition to rob and loot the rest of the world.
This view reflected a fundamental change in emphasis. Whereas
earlier Marxist theorists of imperialism accentuated the centrality of
exploitation in production, dependency and World System analysts shifted
the focus to trade and unequal exchange. And while previous theories
concentrated on the global class struggle, dependency and World System
analyses spoke of a conflict between states and geographical regions. The
new framework, although nominally ‘Marxist’ on the outside, has little
Marxism left on the inside.[12]
And if we are to believe the postists who quickly jumped on the
dependency bandwagon, there is nothing particularly surprising about this
particular theoretical bent. After all, ‘history’ is no more than an
ethno-cultural clash of civilizations, a never-ending cycle of imperial
‘hegemonies’ in which the winners (ego) impose their ‘culture’ on the
losers (alter).[13] To the naked eye, the totalizing capitalization of our
contemporary world may seem like a unique historical process. But don’t be
deceived. This apparent uniqueness is a flash in the pan. Deconstruct it
and what you are left with is yet another imperial imposition – in this
case, the imposition of a Euro-American ‘financialized discourse’ on the
rest of the world.
Red Giant: An Empire
Imploded
The dependency version of the nexus, though, didn’t hold for
long, and in the 1970s the cards again got shuffled. The core stumbled
into a multifaceted crisis: the United States suffered a humiliating
defeat in Vietnam, stagflation decelerated and destabilized the major
capitalist countries and political unrest seemed to undermine the
legitimacy of the capitalist regime itself. In the meantime, the periphery
confounded the theorists: on the one hand, import substitution, the
prescribed antidote to dependency, pushed developing countries, primarily
in Latin America, into a debt trap; on the other hand, the inverse policy
of privatization and export promotion, implemented mostly in East Asia,
triggered an apparent ‘economic miracle’. Taken together, these
developments didn’t seem to sit well with the notion of Western financial
imperialism. And so, once more the nexus had to be
revised.
According to the new script, ‘financialization’ is no longer a
panacea for the imperial power. In fact, it is prime evidence of imperial
decline.
The reasoning here goes back to the basic Marxist distinction
between ‘industrial’ activity on the one hand and ‘commercial’ and
‘financial’ activities on the other. The former activity is considered
‘productive’ in that it generates surplus value and leads to the
accumulation of ‘actual’ capital. The latter activities, by contrast, are
deemed ‘unproductive’; they don’t generate any new surplus value and
therefore, in and of themselves, do not create any ‘actual’
capital.
This distinction – which most Marxists accept as sacrosanct –
has important implications for the nexus of imperialism and financialism.
It is true, say the advocates of the new script, that finance (along with
other forms of waste) helps the imperial core absorb its rising surplus –
and in so doing prevents stagnation and keeps accumulation going. But
there is a price to pay. The addiction to financial waste ends up
consuming the very fuel that sustains the core’s imperial position: it
hollows out the core’s industrial sector, it undermines its productive
vitality, and, eventually, it limits its military capabilities. The
financial sector itself continues to expand absolutely and relatively, but
this is the expansion of a ‘red giant’ (our term) – the final inflation of
a star ready to implode.
The process leading to this implosion is emphasized by theories
of hegemonic transition.[14] The analyses here come in different versions,
but they all seem to agree on the same basic template. According to this
template, the maturation of a hegemonic power – be it Holland in the
seventeenth century, Britain in the nineteenth century or the United
States presently – coincides with the ‘over-accumulation’ of capital (i.e.
the absence of sufficiently profitable investment outlets). This
over-accumulation – along with growing international rivalries, challenges
and conflicts – triggers a system-wide financial expansion, marked by
soaring capital flows, a rise in market speculation and a general
inflation of debt and equity values. The financial expansion itself is led
by the hegemonic state in an attempt to arrest its own decline, but the
reprieve it offers can only be temporary. Relying on finance drains the
core of its energy, causes productive investment to flow elsewhere and
eventually sets in motion the imminent process of hegemonic transition.
Although the narrative here is universal, its inspiration is
clearly drawn from the apparent ‘financialized decline’ of U.S. hegemony.
Since the 1970s, many argue, the country has been ‘depleted’: it has grown
overburdened by military spending; it has gotten itself entangled in
unwinnable armed conflicts, and it has witnessed its industrial-productive
base sucked dry by a Wall Street-Washington Complex that prospers on the
back of rising debt and bloated financial
intermediation.[15]
In order to compensate for its growing weakness, these
observers continue, the United States has imposed its own model of
‘financialization’ on the rest of the world, hoping to scoop the resulting
expansion of liquidity. Some states have been compelled to replicate the
model in their own countries, others states have been tempted to finance
it by buying U.S. assets, and pretty much all states have been pulled into
an unprecedented global whirlpool of capital flow.
The spread of ‘financialization’, though, has only been party
successful. For a while, the United States benefited from being able to
control, manipulate and leverage this expansion for its own ends. But in
the opinion of many, the growing severity of recent financial, economic
and military crises suggests that this ability has been greatly reduced
and that U.S. hegemony is now coming to an end.
The highly publicized nature of these imperial misgivings makes
this latest version of the nexus seems persuasive. But when we look more
closely at the facts, the theoretical surface no longer seems smooth; and
as we get even closer to the evidence, cracks begin to
appear.
Start with the cross-border flow of capital, the international
manifestation of ‘financialization’. This process is often misunderstood,
even by high theorists, so a brief clarification is in order. Contrary to
popular belief, the flow of capital is financial, and only financial. It
consists of legal transactions, whereby investors in one country buy or
sell assets in another – and that is it. There is no flow of material or
immaterial resources, productive or otherwise. The only things that move
are ownership titles.[16]
These changes in ownership, of course, are of great importance.
If the flow of capital is large enough, the stock of foreign owned assets
will grow relative to domestically owned assets. And as the ratio rises,
the ownership of capital becomes increasingly
transnational.
The history of this process, from 1870 to the present, is
sketched in Figure 1, where we plot the total value of all foreign assets
as a percent of global GDP (both denominated in dollars). The underling
numbers, admittedly, are not very accurate. The raw data on foreign
ownership are scarce; often they are of questionable quality; rarely if
ever are they available on a consistent basis; and almost always they
require painstaking research to collate and heroic assumptions to
calibrate. There are also huge problems in estimating global GDP,
particularly for earlier periods. But even if we take these severe
limitations into consideration, the overall picture seems fairly
unambiguous.[17]
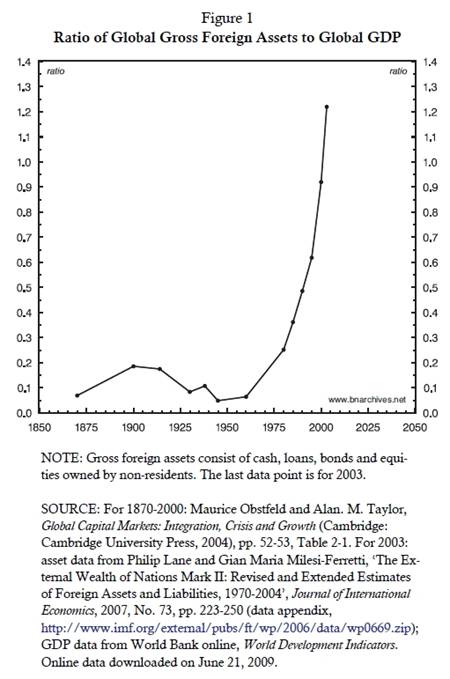
The figure shows three clear periods: 1870-1900, 1900-1960 and
1960-2003. The late nineteenth century, marked by the imperial expansion
of ‘finance capital’, saw the ratio of global foreign assets to global GDP
more than double – from 7% in 1870 to 19% in 1900. This upswing was
reversed during the first half of the twentieth century. The mayhem
created by two world wars and the Great Depression on the one hand and the
emergence of domestic ‘institutionalized waste’ on the other undermined
the flow of capital and caused the share of foreign ownership to recede.
By 1945, with the onset of decolonization under U.S. ‘hegemony’ and the
beginning of the Cold War, the ratio of foreign assets to global GDP hit a
record low of 5%. This was the nadir. The next half century brought a
massive reversal. In the early 1980s, when Ronald Reagan and Margaret
Thatcher announced the beginning of neoliberalism, the ratio of foreign
assets to GDP was already higher than in 1900; and, by 2003, after a
quarter century of exponential growth, it reached an all time high of
122%.
This final number represents a significant level of
transnational ownership. According to recent research by the McKinsey
Global Institute, between 1990 and 2006 the global proportion of
foreign-owned assets has nearly tripled, from 9% to 26% of all world
assets (both foreign and domestically-owned). The increase was broadly
based: foreign ownership of corporate bonds rose from 7% to 21% of the
world total, foreign ownership of government bonds rose from 11% to 31%
and foreign ownership of corporate stocks rose from 9% to
27%.[18]
The next step is to break the aggregate front and examine the
distribution of ownership. This is what we do in Figure 2, which compares
the foreign asset shares of British and U.S. owners from 1825 to the
present. The chart shows two important differences between the earlier era
of ‘classical imperialism’ dominated by Britain and the more recent
‘neo-imperial’ period led by the United States.
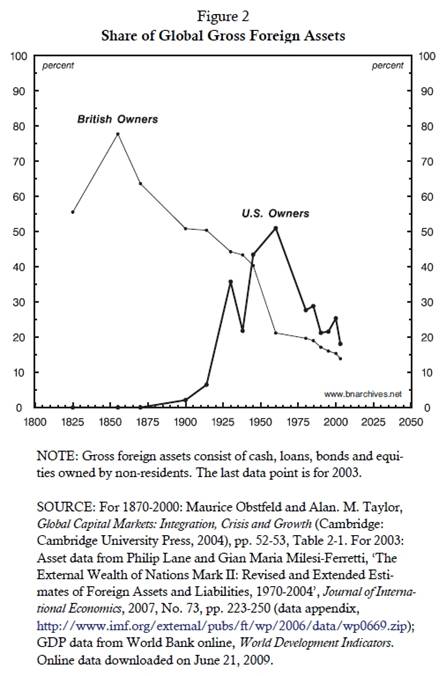
First, there is the pattern of decline. British owners saw
their share of global assets fall from the mid-nineteenth century onward,
but until the end of the century their primacy remained intact. The real
challenge came only in the twentieth century, when capital flow
decelerated sharply and foreign asset positions were unwound; and it was
only in the interwar period, when foreign investment gave way to capital
flight, that the share of British owners fell below
50%.
The U.S. experience was very different. U.S. owners achieved
their primacy right after the Second World War, when capital flow had
already been reduced to a trickle – and that position was undermined the
moment capital flow started to pick up. In 1980, when U.S.
‘financialization’ started in earnest, U.S. owners accounted for only 28%
of global foreign assets. And by 2003, when record capital flow and the
U.S. invasion of Afghanistan and Iraq prompted many Marxists to pronounce
the dawn of an ‘American Empire’, the asset share of U.S. owners was
reduced to a mere 18%.
Second, there is the identity of the leading owners. In the
previous transition, power shifted from owners in one core country
(Britain) to those in another (the United States). By contrast, in the
current transition (assuming one indeed is underway) the contenders are
often from the periphery. In recent years, owners from China, OPEC,
Russia, Brazil, Korea and India, among others, have become major foreign
investors with significant international positions – including large
stakes in America’s ‘imperial’ debt.
Does this shift of foreign ownership represent the rising
hegemony of countries such as China – or is what we are witnessing here
yet another mutation of imperialism? Perhaps, as some observers seem to
imply, we’ve entered a (neo) neo-imperial order in which the ‘Empire’
actually boosts its power by selling off its assets to the
periphery?
The Global Distribution of
Profit
Surprising as it may sound, such a selloff is not inconsistent
with the basic theory of hegemonic transition. To reiterate, according to
this theory, hegemonic transitions are always marked by a financial
explosion which is triggered, led and leveraged by the core in a vain
attempt to arrest its imminent decline. Supposedly, this explosion enables
the hegemonic power to amplify its financial supremacy in order to
(temporarily) retain its core status and power. And if retaining that
power requires the devolution of foreign assets and the selloff of
domestic ones, so be it.
The question is how to assess this power. How do we know
whether the core’s attempt to leverage global ‘financialization’ is
actually working? Is there a meaningful benchmark for power, and how
should this benchmark be used and understood?
Unfortunately, most theorists of hegemonic transitions tend to
avoid the nitty gritty data, so it’s often unclear how they themselves
gauge the shifting trajectories of global power. But given the
hyper-capitalist nature of our epoch, it seems pretty safe to begin with
the bottom line: net profit.
Net profit is the pivotal magnitude in capitalism. It
determines the health of corporations, it tells investors how to
capitalize assets, it sets limits on what government officials feel they
can and cannot do. It is the ultimate yardstick of capitalist power, the
category that subjugates the social individual and makes the whole system
tick. It is the one magnitude than no researcher of capitalism can afford
to ignore.
With this obvious rationale in mind, consider Figure 3, which
traces the distribution of global net profit earned by publicly-traded
corporations. The chart, covering the period from 1974 to the present,
shows three profit series, each denoting the profit share of a distinct
corporate aggregate: (1) firms listed in the United States; (2) firms
listed in developed markets excluding the United States; and (3) firms
listed in the rest of the world – i.e. in ‘emerging
markets’.
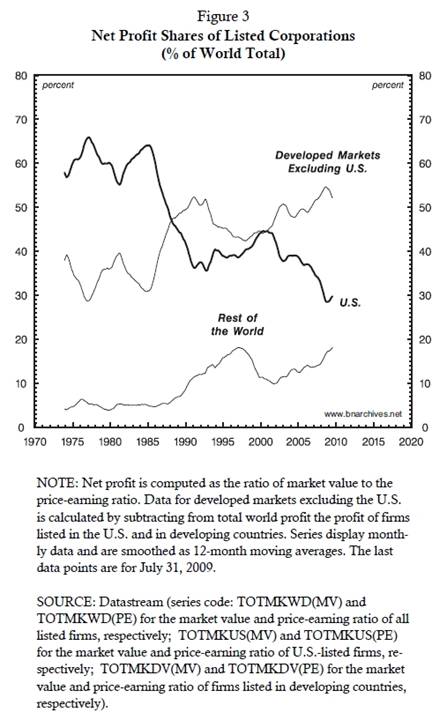
The data demonstrate a sharp reversal of fortune. Until the
mid-1980s, U.S.-listed firms dominated: they scooped roughly 60% of all
net profits, leaving firms listed in other developed markets 35% of the
total and those listed in ‘emerging market’ less than
5%.
But then the tables turned. During the second half of the
1980s, the net profit share of U.S.-listed firms plummeted, falling to 36%
in less than a decade. The 1990s seemed to have stabilized the decline,
but in the early 2000s the downward drift resumed. By the end of the
decade, U.S. firms saw their net profit fall to 29% of the world
total.
The other two aggregates moved in the opposite direction. By
2009, the profits of firms listed in developed countries other than the
U.S. reached 53% of the total, while the share of ‘emerging market’ firms
quadrupled to 18%.
These numbers, of course, should be interpreted with care.
First, note that our profit data here cover only publicly traded firms;
they don’t include unlisted, private firms. This fact means that
variations in profit shares reflect two very different processes: (1)
changes in the amount of profit earned by listed firms, and (2) the pace
of listing and delisting of firms. The latter factor became important
during the late 1980s and 1990s, when Europe and the ‘emerging markets’
saw their stock market listings swell with many private corporations going
public – this at a time when the number of listed firms in the United
States remained flat.
Second, the location of a firm’s listing says nothing about its
operations and owners. Many firms whose shares are traded in the financial
centres of the United States and Europe in fact operate elsewhere. And
then there is the issue of ultimate ownership. Recall that currently one
third of all global assets are owned by foreigners. This proportion is
already large enough to make it difficult to determine the ‘nationality of
capital’, and if it were to rise further the whole endeavour would become
an exercise in futility.
The theoretical implications of these caveats have received
little or no attention from students of hegemonic transitions, and their
quantitative implications remain unclear. But even if we take the
‘nationality of capital’ at face value and consider the numbers in Figure
3 as accurate, it remains obvious that ‘financialization’ has not worked
for the hegemonic power: despite the alleged omnipotence of its Wall
Street-Washington Complex, despite its control over key international
organizations, despite having imposed neoliberalism on the rest of the
world, and despite its seemingly limitless ability to borrow funds and
suck in global liquidity – the bottom line is that the net profit share of
U.S. listed corporations has kept falling and
falling.
The Engine of
‘Financialization’
Now, in and of itself, the collapse of the U.S. profit share –
much like the selloff of U.S. assets – isn’t at odds with the theory of
hegemonic transition. To repeat, this theory suggests that the
hegemonic/imperial power, having been weakened by its prior financial
excesses (among other ills), will kick-start, promote and sustain a
system-wide process of ‘financialization’. According to the theory, the
latent purpose is to leverage this process in order to slow down the
hegemon’s own decline – but nowhere does the theory say that this
‘strategy’, whether conscious or not, has to
succeed.
Presented in this way, the story sounds historically
compelling, logically consistent and empirically convincing – but only if
we can first establish one basic fact. We need to show that the global
process of ‘financialization’ indeed has been led by the United States.
This is the starting point. Only if U.S. ‘financialization’ preceded, was
bigger than and propelled ‘financialization’ in the rest of the world can
we speak of the U.S. leveraging this process for its own ends. And only
then can we assess whether that leveraging succeeded or
failed.
So let’s look at the evidence.
Concepts and Methods
The initial step in this sequence is to measure
‘financialization’. Conceptually, the task may seem simple. All we need to
do is calculate the share of financial activity in overall economic
activity and then trace the trajectory of the resulting ratio. When this
ratio goes up, we can say that the economy is being ‘financialized’; when
it comes down we would conclude that it is being
‘de-financialized’.
But that’s easier said than done.[19]
The basic difficulty is that capitalism is mediated through
money, and that fact makes every mediated activity both ‘economic’ and
‘financial’ at the same time. As we have already seen, heterodox
economists bypass the problem by defining ‘finance’ more narrowly to
denote activities that merely shuffle money and credit without producing
‘real’ goods and services (and obviously without generating any surplus
value and ‘actual capital’). Unfortunately, though, this yardstick isn’t
very practical. In order to use it, the economist needs to know which
activity is ‘productive’ and which is not; and yet, strange as it may
sound, this is something that economists do not – and indeed cannot –
know. Despite hundreds of years of theorizing and endless claims to the
contrary, they remain unable to actually measure ‘productivity’. They
cannot quantify the productivity of the CEO of a large bank – or of an
auto mechanic for that matter. In fact, they don’t even have the units
with which to measure such productivity.
The only thing they can do is to assume. Mainstream economists
assume that productivity is ‘revealed’ by income, so if the CEO earns
1,000 times more than the mechanic, he must be 1,000 more productive.
Marxists reject this arbitrary assumption; instead, they stipulate, also
arbitrarily, that financiers are unproductive while mechanics are
productive – although this claim still leaves them unsure of how to treat
actual corporations, where ‘unproductive’ and ‘productive’ activities are
always inextricably intertwined.
The net result is that we don’t have a clear theoretical
definition for ‘finance’ and therefore no objective way to assess the
extent of ‘financialization’.
But not all is lost.
We certainly can stick with conventions – and the convention,
at least among capitalists and investors, is to treat ‘finance’ as
synonymous with the FIRE sector; i.e. with firms whose primary activities
involve financial intermediation (banking, trust funds, brokerages, etc.),
insurance or real estate.
Based on this conventional (albeit theoretically loose)
definition of finance, and given our specific concern here with capitalist
power, it seems appropriate to proxy the extent and trajectory of
‘financialization’ by looking at the share of total net profit accounted
for by FIRE corporations. The magnitude of this share would indicate the
extent to which FIRE firms have been able to leverage ‘financialization’
for their own end, and the way this share changes over time would tell us
whether their leverage has increased or decreased.
The Inconvenient Facts
This distributional measure of ‘financialization’ is depicted
by the two series in Figure 4. The first series shows the net profit of
FIRE corporations as a percent of the net profit of all U.S.-listed firms.
The second series computes the same ratio for firms listed outside the
United States.
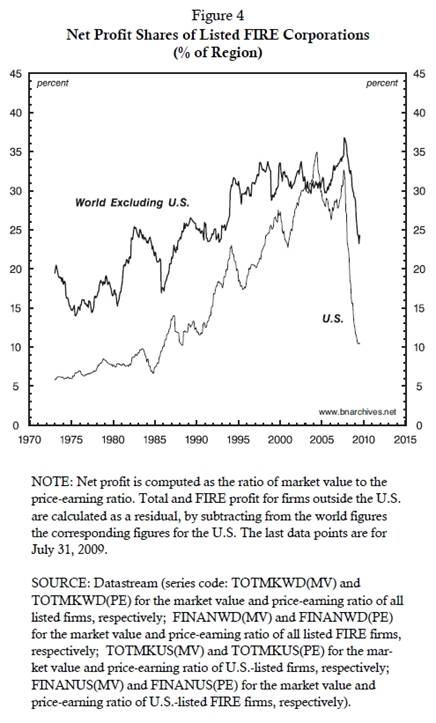
And here we run into a little
surprise.
According to the theory of hegemonic transition, the engine of
‘financialization’ is the United States. This is the black hole of the
World System. It is the site where finance has been used most extensively
to absorb the system’s surplus. It is the seat of the all-powerful Wall
Street-Washington Complex. It is where neoliberal ideology first took
command and from where it was later imposed with force and temptation on
the rest of the world. It is the engine that led, pulled and pushed the
entire process.
But the facts in Figure 4 seem to tell a different story.
According to the chart, the United Sates has not been leading the process.
If anything, it seems to have been ‘dragged’ into the process by the rest
of the world. . . .
During the early 1970s, before the onset of systemic
‘financialization’, the U.S. FIRE sector accounted for 6% of the total net
profit of U.S.-listed firms. At the time, the comparable figure for the
rest of the world was 18% – three times as high! From then on, the United
States was merely playing catch-up. Its pace of ‘financialization’ was
faster than in the rest of the world; but with the sole exception of a
brief period in the late 1990s, its level of ‘financialization’ was always
lower. In other words, if wish to stick with the theory of a
finance-fuelled red giant that is slowly imploding as its peripheral
liquidly runs out, we should apply that theory not to the United States,
but to the rest of the world!
Indeed, even the most recent period of crisis seems at odds
with the theory. According to the conventional creed, both left and right,
the current crisis is payback for the sins of excessive ‘financialization’
and improper bubble blowing.[20] In this Galtonean theory, deviations and
distortions always revert to mean, ensuring that the biggest sinners end
up suffering the most. And since the U.S. FIRE sector was supposedly the
main culprit, it was also the hardest hit.
The only problem is that, according to Figure 4, the U.S.
wasn’t the main culprit. On the eve of the crisis, the extent of
‘financialization’ was greater in the rest of the world than in the U.S.
And yet, although the world’s financiers committed the greater sin, it was
their U.S. counterparts who paid the heftier price. The former saw their
profit share decline mildly from 37% to 25% of the total, while the latter
watched their own share crash from 32% to 10%.
The gods of finance must have their own sense of
justice.
The End of a Nexus?
Of course, this isn’t the first time that a monkey wrench has
been thrown into the wheels of the ever-changing nexus of imperialism and
financialism. As we have seen, over the past century the nexus had to be
repeatedly altered and transformed to match the changing reality. Its
first incarnation explained the imperialist scramble for colonies to which
finance capital could export its ‘excessive’ surplus. The next version
talked of a neo-imperial world of monopoly capitalism where the core’s
surplus is absorbed domestically, sucked into a ‘black hole’ of military
spending and financial intermediation. The third script postulated a World
System where surplus is imported from the dependent periphery into the
financial core. And the most recent edition explains the hollowing out of
the U.S. core, a ‘red giant’ that had already burned much of its own
productive fuel and is now trying to ‘financialize’ the rest of the world
in order to use the system’s external liquidity.
Yet, here, too, the facts refuse to cooperate: contrary to the
theory, they suggest that U.S. ‘Empire’ has followed rather than led the
global process of ‘financialization’ and that U.S. capitalists have been
less dependent on finance than their peers
elsewhere.
Of course, this inconvenient evidence could be dismissed as
cursory – or, better still, neutralized by again adjusting the meaning of
imperialism and financialism to fit the new reality. But maybe it’s time
to stop the carousel and cease the repeated retrofits. Perhaps we need to
admit that, after a century of transmutations, the nexus of imperialism
and financialism has run its course, and that we need a new framework
altogether.
Jonathan Nitzan and Shimshon
Bichler are co-authors of Capital as Power: A Study of Order and
Creorder, RIPE series in Global Political Economy (London and New York:
Routledge, 2009). All their publications are freely available from The
Bichler & Nitzan Archives
(http://bnarchives.net)
Endnotes
[1] The precise terms are rather loose and their use varies
across theorists and over time. Imperialism, empire and colonialism are
used interchangeably, as are finance, fictitious capital finance capital,
financialization and financialism. Here we use imperialism and
financialism simply because they rhyme.
[2] John. A. Hobson, Imperialism: A Study (Ann Arbor:
University of Michigan Press, 1902 [1965]); Rosa Luxemburg, The
Accumulation of Capital, with an introduction by Joan Robinson, translated
by A. Schwarzschild (New Haven: Yale University Press, 1913 [1951]);
Rudolf Hilferding, Finance Capital: A Study of the Latest Phase of
Capitalist Development, edited with an introduction by Tom Bottomore, from
a translation by Morris Watnick and Sam Gordon (London: Routledge &
Kegan Paul, 1910 [1981]); Vladimir I. Lenin, ‘Imperialism, The Highest
State of Capitalism’, in Essential Works of Lenin. ‘What Is to Be Done?’
and Other Writings (New York: Dover Publications, Inc., 1917 [1987]), pp.
177-270; Karl Kautsky, ‘Ultra-Imperialism’, New Left Review, 1970, No. 59
(Jan/Feb), pp. 41-46 (original German version published in
1914).
[3] See, for example, Joseph A. Schumpeter, Imperialism and
Social Classes, with an introduction by Bert Hoselitz, translated by Heinz
Norden (New York: Meridian Books, 1919; 1927 [1955]); Barbara Wertheim
Tuchman, The Guns of August (New York: Macmillan, 1962) and The Proud
Tower: A Portrait of the World Before the War, 1890-1914 (New York:
Macmillan, 1966); and Paul M. Kennedy, The Rise and Fall of the Great
Powers (New York: Random House, 1987), Ch. 5.
[4] Some of the important contributions to this literature
include Josef Steindl, Maturity and Stagnation in American Capitalism (New
York: Monthly Review Press, 1952 [1976]); Shigeto Tsuru, ‘Has Capitalism
Changed?’ in Has Capitalism Changed? An International Symposium on the
Nature of Contemporary Capitalism, edited by S. Tsuru (Tokyo: Iwanami
Shoten, 1956), pp. 1-66. Paul A. Baran and Paul M. Sweezy, Monopoly
Capital: An Essay on the American Economic and Social Order (New York:
Modern Reader Paperbacks, 1966); and Harry Magdoff, The Age of
Imperialism: The Economics of U.S. Foreign Policy, 1st Modern Reader ed.
(New York: Monthly Review Press, 1969).
[5] Veblen’s early analysis is articulated in The Theory of
Business Enterprise (Clifton, New Jersey: Augustus M. Kelley, Reprints of
Economics Classics, 1904 [1975]).
[6] See U.S. National Security Council, NSC 68: United States
Objectives and Programs for National Security. A Report to the President
Pursuant to the President's Directive of January 31, 1950. Top Secret
(Washington DC, 1950); David A. Gold, ‘The Rise and Fall of the Keynesian
Coalition’, Kapitalistate, 1977, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 129-161; and Jonathan
Nitzan and Shimshon Bichler, ‘Cheap Wars’, Tikkun, August 9,
2006.
[7] Classical Marxists interpret the role of waste rather
differently. In their account, wasteful spending withdraws surplus from
the accumulation process; this withdrawal reduces the pace at which
constant capital accumulates; and that reduction lessens the tendency of
the rate of profit to fall. See for example Michael Kidron, Capitalism and
Theory (London: Pluto Press, 1974).
[8] Perhaps the clearest advocate of this argument was the late
Harry Magdoff, a writer whose empirical and theoretical studies stand as a
beacon of scientific research; for a summary, see his Imperialism Without
Colonies (New York: Monthly Review Press, 2003). Similar claims (minus the
research) are offered by Ellen Meiksins Wood, Empire of Capital (London
and New York: Verso, 2003).
[9] Some of the important texts here include Raúl Prebisch, The
Economic Development of Latin America and its Principal Problems (New
York: United Nations, 1950); Paul A. Baran, The Political Economy of
Growth (New York and London: Modern Reader Paperbacks, 1957); Andre Gunder
Frank, Capitalism and Underdevelopment in Latin America: Historical
studies of Chile and Brazil (New York: Monthly Review Press, 1967);
Arghiri Emmanuel, Unequal Exchange. A Study of the Imperialism of Trade
(New York: Monthly Review Press, 1972); Eduardo H. Galeano, Open Veins of
Latin America: Five Centuries of the Pillage of a Continent (New York:
Monthly Review Press, 1973). Samir Amin, Accumulation on a World Scale: A
Critique of the Theory of Underdevelopment. 2 vols. (New York: Monthly
Review Press. 1974); Immanuel Maurice Wallerstein, The Modern
World-System. Capitalist Agriculture and the Origins of the European
World-Economy in the Sixteenth Century (New York: Academic Press, 1974)
and The Modern World-System II: Mercantilism and the Consolidation of the
European World-Economy, 1600-1750 (New York: Academic Press, 1980); and
Fernando Henrique Cardoso and Enzo Faletto, Dependency and Development in
Latin America (Berkeley: University of California Press,
1979).
[10] The inverted commas in this paragraph highlight concepts
that the theory of unequal exchange can neither define nor measure. Since
nobody knows the correct value of labour power, it is impossible to
determine the extent of ‘exploitation’ in the two regions. Similarly,
since no one knows the ‘true’ value of commodities, there is no way to
assess the extent to which export and import prices are ‘high’ or ‘low’.
This latter ignorance makes it impossible to gauge the degree to which the
terms of trade are ‘distorted’ and, indeed, in whose favour; and given
that we don’t know the magnitude or even the direction of the
‘distortion’, it is impossible to tell whether surplus flows from the
periphery to the core or vice versa, and how large the flow might
be.
[11] W.W. Rostow, The Stages of Economic Growth: A
Non-Communist Manifesto (Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press,
1960).
[12] The question of what constitutes a ‘proper’ Marxist
framework is highlighted in the debates over the transition from feudalism
to capitalism. Important contributions to these debates are Maurice Dobb,
Studies in the Development of Capitalism. London: Routledge & Kegan
Paul Ltd., 1946. [1963]); Paul M. Sweezy ‘A Critique’, in The Transition
from Feudalism to Capitalism, Introduction by Rodney Hilton, edited by R.
Hilton (London: Verso, 1950 [1978]); Robert Brenner, ‘The Origins of
Capitalist Development: A Critique of Neo-Smithian Marxism’, New Left
Review, 1977, No. 104 (July-August), pp. 25-92; and Robert Brenner, ‘Dobb
on the Transition from Feudalism to Capitalism’, Cambridge Journal of
Economics, 1978, Vol. 2, No. 2 (June), pp. 121-140. For edited volumes on
this issue, see Rodney Hilton, ed., The Transition from Feudalism to
Capitalism, Introduction by Rodney Hilton (London: Verso, 1978); and T. H.
Aston and C. H. E. Philpin, eds., The Brenner Debate: Agrarian Class
Structure and Economic Development in Pre-Industrial Europe (Cambridge and
New York: Cambridge University Press, 1985).
[13] For a typical narrative, see John M. Hobson, The Eastern
Origins of Western Civilisation. (Cambridge, UK and New York: Cambridge
University Press. 2004).
[14] See for example, Fernand Braudel, Civilization &
Capitalism, 15th-18th Century, translated from the French and revised by
Sian Reynolds, 3 vols. (New York: Harper & Row, Publishers, 1985);
Immanuel Maurice Wallerstein, The Politics of the World-Economy: The
States, the Movements, and the Civilizations (Cambridge, New York and
Paris: Cambridge University Press and Editions de la Maison des sciences
de l'homme, 1984); and Giovanni Arrighi, The Long Twentieth Century:
Money, Power, and the Origins of Our Times. London: Verso,
1994.
[15] For the ‘depletion thesis’, see for example Seymour
Melman, Pentagon Capitalism: The Political Economy of War, 1st ed. (New
York: McGraw-Hill, 1970) and The Permanent War Economy: American
Capitalism in Decline (New York: Simon and Schuster, 1974). A broader
historical application is given in Paul M. Kennedy, The Rise and Fall of
the Great Powers (New York, NY: Random House: 1987).
[16] The generalization here applies to portfolio as well as
direct foreign investment. Both are financial transactions, pure and
simple. The only difference between them is their relative size:
typically, investments that account for less than 10% of the acquired
property are considered portfolio, whereas larger investments are
classified as direct. The flow of capital, whether portfolio or direct,
may or may not be followed by the creation of new productive capacity. But
the creation of such capacity, if and when it happens, is conceptually
distinct, temporally separate and causally independent from the mere act
of foreign investment.
[17] The early data on foreign assets are incomplete in that
they do not cover all countries (especially smaller ones). As a result,
the measured ratio of foreign assets to global GDP in the earlier years of
the chart may be somewhat understated (see Maurice Obstfeld and Alan. M.
Taylor, Global Capital Markets: Integration, Crisis and Growth [Cambridge:
Cambridge University Press, 2004], pp. 51-57).
[18] See Diana Farrell, Susan Lund, Christian Fölster, Raphael
Bick, Moira Pierce, and Charles Atkins, Mapping Global Capital Markets.
Fourth Annual Report (San Francisco: McKinsey Global Institute, January
2008), p. 73, Exhibit 3.10.
[19] For a detailed analysis of the associated difficulties and
impossibilities that we discuss here only in passing, see Jonathan Nitzan
and Shimshon Bichler, Capital as Power: A Study of Order and Creorder (New
York and London: Routledge, 2009), Chs. 6-8 and 10; and Shimshon Bichler
and Jonathan Nitzan, ‘Contours of Crisis II: Fiction and Reality’, Dollars
& Sense, April 28, 2009.
[20] See Shimshon Bichler and Jonathan Nitzan, ‘Contours of Crisis: Plus ça change, plus c'est pareil?’ Dollars & Sense, December 29, 2008; and ‘Contours of Crisis II: Fiction and Reality’, Dollars & Sense, April 28, 2009.